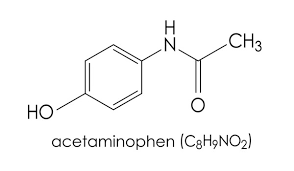
Acetaminophen Background
Acetaminophen has long been renowned for its fever-reducing and pain-relieving capabilities since its introduction in 1955, quickly becoming one of the top OTC drugs due to its usefulness and minimal side effects when taken as directed. Acetaminophen can effectively ease mild to moderate headache pain along with arthritis or menstrual cramps while simultaneously decreasing a fever and relieving cold or flu symptoms.
Tylenol has long been controversial due to the risk of liver damage and overdose; so in 2011, the US FDA (Food and Drug Administration) issued new guidelines regarding its use, seeking to decrease liver injury risks by decreasing dosage caps prescribed and adding warning labels on products containing acetaminophen.
Though safety precautions exist, concerns still exist for acetaminophen when taken alongside multiple medicines or when treating liver conditions. Recent years have witnessed calls for greater regulation and awareness about potential risks related to acetaminophen use, yet its usage remains widespread for pain relief and fever reduction purposes; users need to remain cognizant of any possible side effects so as to take it according to instructions.
At all times it is critical for users to remain aware of potential dangers related to acetaminophen’s use in order to ensure safe dosage instructions and safe administration of its dose instructions. Its effects when used alongside multiple medicines simultaneously or treatment plans are well understood.
acetaminophen can generally be considered safe and effective when taken as directed; however, misuse may result in adverse side effects on health.